An untreated fungal growth in the nails can be significantly problematic. A fungus can affect not only the nail itself, but can also cause damage to the entire nail area, including the nail bed and matrix. Nail tinea can cause the nails to become deformed. Not only do these nails tend to be cosmetically unacceptable, but they may be uncomfortable. Fingernail tinea can sometimes interfere with proper hand function. In the case of toenail tinea, people can have difficulty wearing their usual shoes. Nail tinea can act as a source of fungal infection for the skin. Tinea of the skin can act as an entry point for bacteria. Patients with diabetes or peripheral vascular disease require special consideration. Cellulitis of the lower legs is a serious bacterial skin and soft tissue infection that can cause significant morbidity in these patients.
A number of different types of organism may infect the nail:
- Moulds (dermatomycosis)
- Yeasts
- Dermatophyte fungi (dermatophytosis)
The most common dermatophyte to cause infection of the nails is Trichophytum rubrum. This organism causes 90% of toenail and 50% of fingernail dermatophyte infections.
Nail Fungus Signs
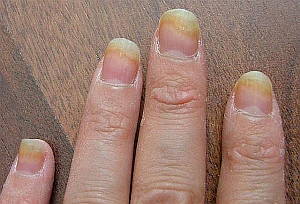
- Yellow/white changes in one or more nails
- Discoloured streaks on the nails
- Scaling or thickening beneath a nail
- Nail plate thickening
- Lifting of the nail from its bed
- The nail pits and flakes
- Nail crumbling
Treating Nail Fungal Infections
A dermatologist can diagnose the type of nail fungi that you have. An appropriate treatment plan may then be developed. It is important to note that some fungal infections can be very challenging to eradicate.
Here are a few things to be mindful of when treating nail fungal infections:
- Fingernail infections tend to be easier to eliminate than toenail infections.
- Toenails take 12 months and fingernails take 6-9 months to grow out.
- It is very important to consider sources of re-infection: these sources include communal showers, old shoes and socks, other family members.
- Around 80% of mild infections can be remedied via a topical treatment.
- Fungus grows well in warm and wet environments: people whose feet are constantly wet will find that it is more difficult to eradicate the tinea.
- Infections involving a significant proportion of the nail plate respond best to oral therapies.
- Laser treatments; this is a medication-free option. It is more expensive than traditional therapies. At least 2 t 5 treatments are often required.
- Nail removal is an option in recalcitrant cases. This can be performed by either surgery, or chemical (urea) application. Antifungal agents are an important adjunct in these cases.
- The cure rate for any treatment modality is generally 65-75%.
If you have any questions or concerns about nail fungus Contact us today.



