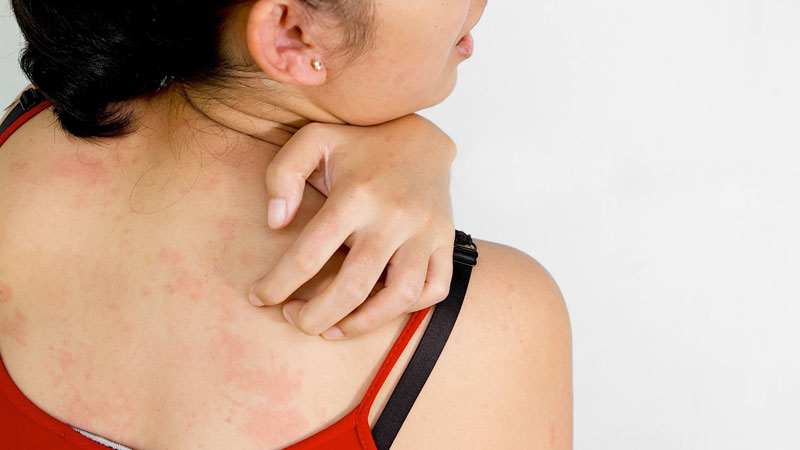
Urticaria is the medical term for what we know as hives. It is an itchy, red rash with raised bumps or welts on the skin. It is a very common medical condition. 10 – 20% of people will have at least one episode in their lifetime. In most people, hives go away within a few days to a few weeks. Occasionally, a person will continue to have urticaria for many years.
Allergies are a common cause of urticaria. However, if the urticaria has persisted for more than 6 weeks, an allergic cause is unlikely. The exact cause of long-term urticaria is as yet unknown, with current theories focusing on an auto-immune response.
Physiology
The bumps on the skin in urticaria are often called ‘wheals’. The wheals are caused by the release of histamine from specialised allergy cells called mast cells. Histamine causes fluid to leak from blood vessels, causing the wheals on the surface of the skin.
Causes of Urticaria
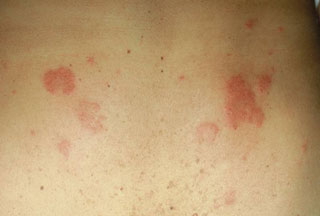 Acute cases of urticaria last less than 6 weeks and the overwhelming majority of cases are the result of an allergic reaction. Viruses can also sometimes cause urticaria. Some of the following are identified causes or triggers:
Acute cases of urticaria last less than 6 weeks and the overwhelming majority of cases are the result of an allergic reaction. Viruses can also sometimes cause urticaria. Some of the following are identified causes or triggers:
- Medications (penicillins, aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
- Insect bites
- Certain foods (shellfish, peanuts and other nuts)
- Viruses
- Exercise
- Cold or heat
- Sun exposure
- Stress
- Scratching
Chronic urticaria lasts more than 6 weeks and is often not associated with an allergic response. For many cases of urticaria, no cause is identified. These cases are termed idiopathic urticaria. For some other cases, some of the causes which have been identified or proposed include:
- Autoimmune disease
- Connective tissue disease
- Hormonal factors
- Infections
- Autoimmune thyroid disease
Urticaria Treatment
In cases of allergic urticaria, it is important to avoid known triggers wherever possible. An Epi-pen is advised for people who suffer from anaphylactic reactions in association with urticaria. Taking an anti-histamine tablet on a regular basis can help alleviate symptoms. However, they may not be 100% effective. Anti-histamines work by inhibiting the release of histamine from mast cells. If anti-histamines are not effective, then other oral therapies may be prescribed in severe cases of urticaria.
If you have any questions or concerns about urticaria contact your local doctor, who will arrange for you to see a dermatologist. Contact us today.